Multiscale estimators
- structure_factor.multiscale_estimators.multiscale_estimator(point_pattern, estimator, subwindows_list, k_list, mean_poisson, m=None, proba_list=None, verbose=True, **kwargs)[source]
Sample from \(Z\) [HGBLachiezeR22] using a PointPattern and a realization from the r.v. \(M\). See the definition of \(Z\) below.
- Parameters
point_pattern (
PointPattern) – An encapsulation of a realization of a point process, the observation window, and (optionally) the intensity of the point process.estimator (str) – Choice of structure factor’s estimator. The parameters of the chosen estimator must be added as keyword arguments. The available estimators are “scattering_intensity”, “tapered_estimator”, “bartlett_isotropic_estimator”, and “quadrature_estimator_isotropic”. See
StructureFactor.subwindows_list (list) – List of increasing cubic or ball-shaped
AbstractSpatialWindow, typically, obtained usingsubwindows_list(). The shape of the windows depends on the choice of theestimator. Each element ofpoint_pattern_listwill be restricted to these windows to compute \(Z\).k_list (list) – List of wavevectors (or wavenumbers) where the
estimatoris to be evaluated. Each element is associated with an element ofsubwindows_list. Typically, obtained usingsubwindows_list().mean_poisson (int) – Parameter of the Poisson r.v. \(M\) used to compute \(Z\). To use a different distribution of the r.v. \(M\), set
mean_poisson=Noneand specifym_listandproba_listcorresponding to \(M\).m (int, optional) – Realization of the positive integer-valued r.v. \(M\) used when
mean_poisson=None. Defaults to None.proba_list (list, optional) – List of \(\mathbb{P}(M \geq j)\) used with
mwhenmean_poisson=None. Should contains at leastmelements. Defaults to None.verbose (bool, optional) – If “True” and
mean_poissonis not None, print the re-sampled values of \(M\). Defaults to False.
- Keyword Arguments
kwargs (dict) – Parameters of the chosen
estimatorof the structure factor. SeeStructureFactor.- Returns
The obtained value of \(Z\).
- Return type
float
Example
from structure_factor.data import load_data from structure_factor.multiscale_estimators import subwindows_list, multiscale_estimator # PointPattern point_pattern = load_data.load_ginibre() window = point_pattern.window # subwindows and k l_0 = 40 subwindows_list, k = subwindows_list(window, subwindows_type="BoxWindow", param_0=l_0) # multiscale_estimator mean_poisson = 85 z = multiscale_estimator(point_pattern, estimator="scattering_intensity", k_list=k, subwindows_list=subwindows_list, mean_poisson=mean_poisson) z
DefinitionLet \(\mathcal{X} \in \mathbb{R}^d\) be a stationary point process of which we consider an increasing sequence of sets \((\mathcal{X} \cap W_m)_{m \geq 1}\), with \((W_m)_m\) centered box (or ball)-shaped windows s.t. \(W_s \subset W_r\) for all \(0< s<r\), and \(W_{\infty} = \mathbb{R}^d\). We define the sequence of r.v. \(Y_m = 1\wedge \widehat{S}_m(\mathbf{k}_m^{\text{min}})\), where \(\widehat{S}_m\) is one of the positive, asymptotically unbiased estimators of the structure factor of \(\mathcal{X}\) applied on the observation \(\mathcal{X} \cap W_m\), and \(\mathbf{k}_m^{\text{min}}\) is the minimum allowed wavevector associated with \(W_m\). Then, \(Z\) is defined by,
\[Z = \sum_{j=1}^{M} \frac{Y_j - Y_{j-1}}{\mathbb{P}(M\geq j)}\]with \(M\) an \(\mathbb{N}\)-valued random variable such that \(\mathbb{P}(M \geq j)>0\) for all \(j\), and \(Y_{0}=0\) [HGBLachiezeR22], [RG15].
- structure_factor.multiscale_estimators.coupled_sum_estimator(y_list, proba_list)[source]
The coupled sum estimator of [RG15].
- Parameters
y_list (list) – List of \(M\) realizations of the r.v. \(Y\).
proba_list (list) – List of \(\mathbb{P}(M \geq j)\) with \(1 \leq j \leq M\).
- Returns
Obtained value of the coupled sum estimator.
- Return type
float
Example
from structure_factor.multiscale_estimators import coupled_sum_estimator y_list= [3, 2.5, 1.2433, 0.1] proba_list = [0.5, 0.4, 0.333, 0.21232] z = coupled_sum_estimator(y_list, proba_list) z
DefinitionLet \((Y_m)_{m\geq 1}\) be a sequence of \(L^2\) approximations of a r.v. \(Y\) each of which can be generated in finite time, for which \(\mathbb{E}^{1/2}[(Y_m - Y)^2]\) converges to zero as \(m\) goes to infinity. The coupled sum estimator of [RG15] is defined by,
\[Z = \sum_{j=1}^{M} \frac{Y_j - Y_{j-1}}{\mathbb{P}(M\geq j)},\]with \(M\) an \(\mathbb{N}\)-valued random variable such that \(\mathbb{P}(M \geq j)>0\) for all \(j\), and \(Y_{0}=0\).
- structure_factor.multiscale_estimators.subwindows_list(window, subwindows_type='BoxWindow', param_0=None, param_max=None, params=None)[source]
Create a list of cubic (or ball)-shaped subwindows of a father window, with the associated minimum allowed wavevectors (or wavenumbers).
- Parameters
window (
AbstractSpatialWindow) – Father window.subwindows_type (str, optional) – Type of the subwindows to be created. The available types are “BoxWindow” and “BallWindow”. The former for cubic and the latter for ball-shaped subwindows. Defaults to “BoxWindow”.
param_0 (float, optional) – Parameter (lengthside/radius) of the first subwindow to be created. If not None, an increasing sequence of subwindows with parameters of unit increments is created. The biggest subwindow has parameter
param_maxif it’s not None, else, the maximum possible parameter. Defaults to None.param_max (float, optional) – Maximum subwindow parameter (lengthside/radius). Used when
param_0is not None. Defaults to None.params (list, optional) – List of parameters (lengthside/radius) of the output subwindows. For a list of parameters of unit increments,
param_0andparam_maxcan be used instead. Defaults to None.
- Returns
subwindows: Obtained subwindows.
k: Minimum allowed wavevectors of
allowed_k_scattering_intensity()or wavenumbers ofallowed_k_norm_bartlett_isotropic()associated with the subwindow list. The former is for cubic and the latter for ball-shaped subwindows.
- Return type
(list, list)
Example
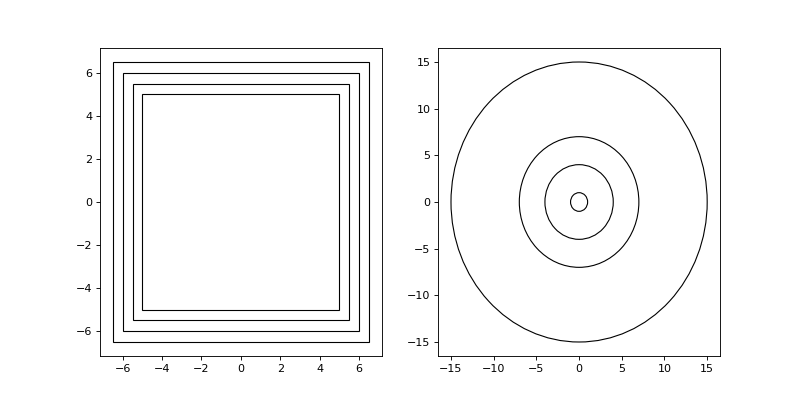
from structure_factor.spatial_windows import BoxWindow from structure_factor.multiscale_estimators import subwindows_list # Example 1: L = 30 window = BoxWindow([[-L / 2, L / 2]] * 2) # subwindows and k l_0 = 10 subwindows_box, k = subwindows_list(window, subwindows_type="BoxWindow", param_0=l_0) # Example 2: subwindows_params=[1, 4, 7, 15] subwindows_ball, k_norm = subwindows_list(window, subwindows_type="BallWindow", params=subwindows_params) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig, axis = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10,5)) axis[0].plot(0,0) axis[1].plot(0,0) for i, j in zip(subwindows_box, subwindows_ball): i.plot(axis=axis[0]) j.plot(axis=axis[1]) plt.show()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
- structure_factor.multiscale_estimators.m_threshold(window_min, window_max)[source]
Find the maximum number of integers ranging between the parameters (lengthside/radius) of
window_minand the largest subwindow ofwindow_maxhaving the shape ofwindow_min. In particular, it gives the maximum value of the r.v. \(M\) that can be used to compute themultiscale_estimator()given the smallest and biggest subwindow.- Parameters
window_min (
AbstractSpatialWindow) – Smallest cubic or ball-shaped window centered at the origin.window_max (
AbstractSpatialWindow) – Biggest box or ball-shaped window centered at the origin.
- Returns
Maximum number of integers ranging between the parameters (lengthside/radius) of
window_minand the largest subwindow ofwindow_maxhaving the shape ofwindow_min.- Return type
int
Example
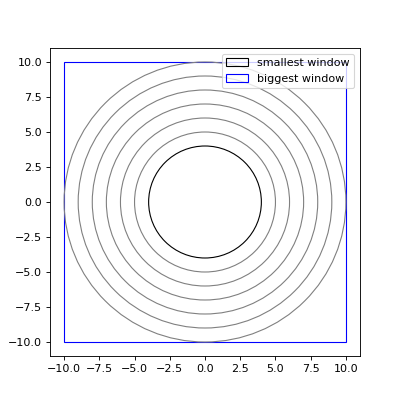
from structure_factor.spatial_windows import BoxWindow, BallWindow from structure_factor.multiscale_estimators import m_threshold window_min = BallWindow(center=[0,0], radius=4) window_max = BoxWindow(bounds=[[-10, 10], [-10, 10]]) m_thresh = m_threshold(window_min, window_max) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig, axis = plt.subplots( figsize=(5,5)) axis.plot(0,0) window_min.plot(axis=axis, color="k", label="smallest window") window_max.plot(axis=axis, color="b", label="biggest window") for j in range(1, m_thresh+1): w = BallWindow(center=[0,0], radius=4+j) w.plot(axis=axis, color="grey") axis.legend() plt.show()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
See also