Structure factor
Class collecting estimators of the structure factor \(S(\mathbf{k})\) of stationary point process given one realization encapsulated in a PointPattern.
The available estimators:
scattering_intensity(): The scattering intensity and the corresponding debiased versions.tapered_estimator(): The tapered or multitapered estimator and the corresponding debiased versions.tapered_estimator_isotropic(): Bartlett’s isotropic estimator.quadrature_estimator_isotropic(): Integral estimation using Hankel transform quadrature.
The available plot methods:
plot_non_isotropic_estimator(): Visualize the results ofscattering_intensity(),tapered_estimator(), ormultitapered_estimator().plot_isotropic_estimator(): Visualize the results oftapered_estimator_isotropic()orquadrature_estimator_isotropic().
For the theoretical derivation and definitions of these estimators, we refer to [HGBLachiezeR22].
- class structure_factor.structure_factor.StructureFactor(point_pattern)[source]
Bases:
objectImplementation of various estimators of the structure factor \(S(\mathbf{k})\) of a stationary point process given one realization encapsulated in the
point_patternattribute.DefinitionThe structure factor \(S\) of a d-dimensional stationary point process \(\mathcal{X}\) with intensity \(\rho\) is defined by,
\[S(\mathbf{k}) = 1 + \rho \mathcal{F}(g-1)(\mathbf{k}),\]where \(\mathcal{F}\) denotes the Fourier transform, \(g\) the pair correlation function of \(\mathcal{X}\), \(\mathbf{k}\) a wavevector of \(\mathbb{R}^d\). For more details we refer to [HGBLachiezeR22], (Section 2) or [Tor18], (Section 2.1, equation (13)).
- __init__(point_pattern)[source]
Initialize StructureFactor from
point_pattern.- Parameters
point_pattern (
PointPattern) – Object of type point pattern which contains a realizationpoint_pattern.pointsof a point process, the window where the points were simulatedpoint_pattern.windowand (optionally) the intensity of the point processpoint_pattern.intensity.
- property dimension
Ambient dimension of the underlying point process.
- scattering_intensity(k=None, debiased=True, direct=True, **params)[source]
Compute the scattering intensity \(\widehat{S}_{\mathrm{SI}}\) estimate of the structure factor from one realization of a stationary point process encapsulated in the
point_patternattribute.- Parameters
k (numpy.ndarray, optional) – Array of size \(n \times d\) where \(d\) is the dimension of the space, and \(n\) is the number of wavevectors where the scattering intensity is evaluated. If
k=Noneanddebiased=True, the scattering intensity will be evaluated on the corresponding set of allowed wavevectors; In this case, the keyword argumentsk_max, andmeshgrid_shapecan be used. Defaults to None.debiased (bool, optional) –
Trigger the use of a debiased tapered estimator. Defaults to True. If
debiased=True, the estimator is debiased as follows,if
k=None, the scattering intensity will be evaluated on the corresponding set of allowed wavevectors.if
kis not None anddirect=True, the direct debiased scattering intensity will be used,if
kis not None anddirect=False, the undirect debiased scattering intensity will be used.
direct (bool, optional) – If
debiasedis True, trigger the use of the direct/undirect debiased scattering intensity. Parameter related todebiased. Defaults to True.
- Keyword Arguments
params (dict) – Keyword arguments
k_maxandmeshgrid_shapeofallowed_k_scattering_intensity(), used whenk=Noneanddebiased=True.- Returns
k: Wavevector(s) on which the scattering intensity has been evaluated.
estimation: Evaluation of the scattering intensity estimator of the structure factor at
k.
- Return type
tuple(numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray)
Example
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from structure_factor.point_processes import HomogeneousPoissonPointProcess from structure_factor.spatial_windows import BoxWindow from structure_factor.structure_factor import StructureFactor point_process = HomogeneousPoissonPointProcess(intensity=1 / np.pi) window = BoxWindow([[-50, 50], [-50, 50]]) point_pattern = point_process.generate_point_pattern(window=window) sf = StructureFactor(point_pattern) k, sf_estimated = sf.scattering_intensity(k_max=4) sf.plot_non_isotropic_estimator( k, sf_estimated, plot_type="all", error_bar=True, bins=30, exact_sf=point_process.structure_factor, scale="log", label=r"$\widehat{S}_{\mathrm{SI}}(\mathbf{k})$", ) plt.tight_layout(pad=1)
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
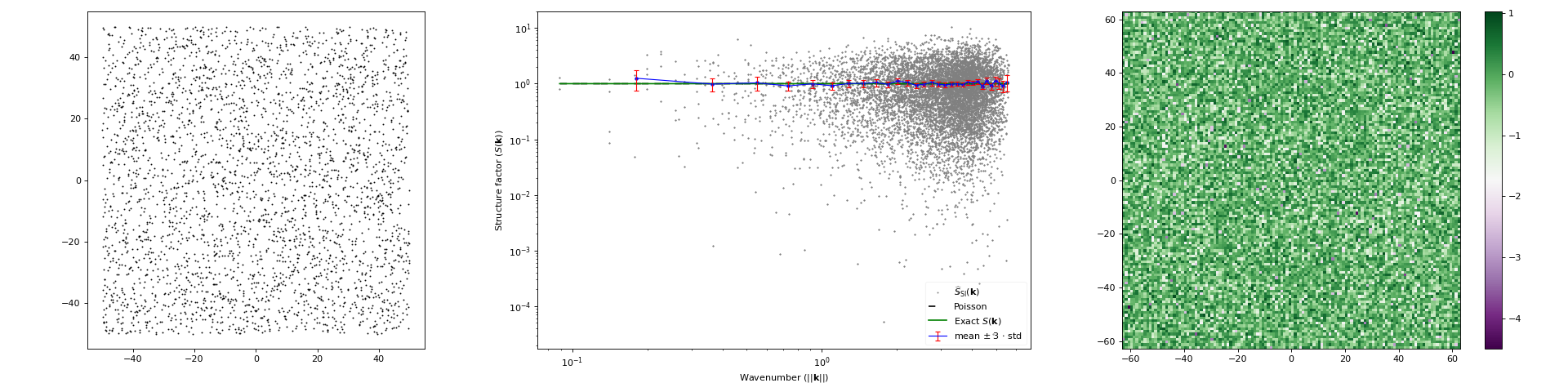 Definition
DefinitionThe scattering intensity \(\widehat{S}_{\mathrm{SI}}\) is an estimator of the structure factor \(S\) of a stationary point process \(\mathcal{X} \subset \mathbb{R}^d\) with intensity \(\rho\). It is computed from one realization \(\mathcal{X}\cap W =\{\mathbf{x}_i\}_{i=1}^N\) of \(\mathcal{X}\) within a box window \(W=\prod_{j=1}^d[-L_j/2, L_j/2]\).
\[\widehat{S}_{\mathrm{SI}}(\mathbf{k}) = \frac{1}{N}\left\lvert \sum_{j=1}^N \exp(- i \left\langle \mathbf{k}, \mathbf{x_j} \right\rangle) \right\rvert^2 .\]For more details we refer to [HGBLachiezeR22], (Section 3.1).
Note
Typical usage
If the observation window is not a
BoxWindow, use the methodrestrict_to_window()to extract a sub-sample in aBoxWindow.
- tapered_estimator(k, tapers, debiased=True, direct=True)[source]
Compute the (multi)tapered estimator parametrized by
tapersof the structure factor of a stationary point process given a realization encapsulated inpoint_pattern.- Parameters
k (numpy.ndarray) – Array of size \(n \times d\) where \(d\) is the dimension of the space, and \(n\) is the number of wavevectors where the tapered estimator is evaluated.
t1 – sequence of concrete tapers with methods
.taper(x, window)corresponding to the taper function \(t(x, W)\) , and.ft_taper(k, window)corresponding to the Fourier transform \(\mathcal{F}[t(\cdot, W)](k)\) of the taper. See also Tapers.t2 – sequence of concrete tapers with methods
.taper(x, window)corresponding to the taper function \(t(x, W)\) , and.ft_taper(k, window)corresponding to the Fourier transform \(\mathcal{F}[t(\cdot, W)](k)\) of the taper. See also Tapers.... – sequence of concrete tapers with methods
.taper(x, window)corresponding to the taper function \(t(x, W)\) , and.ft_taper(k, window)corresponding to the Fourier transform \(\mathcal{F}[t(\cdot, W)](k)\) of the taper. See also Tapers.debiased (bool, optional) – Trigger the use of a debiased estimator. Defaults to True.
direct (bool, optional) – If
debiasedis True, trigger the use of the direct/undirect debiased tapered estimator. Parameter related todebiased. Defaults to True.
- Returns
k: Wavevector(s) on which the tapered estimator has been evaluated.
estimation: Evaluation of the tapered estimator at
k..
- Return type
tuple(numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray)
Note
Calling this method with its default arguments is equivalent to calling
scattering_intensity().Example
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from structure_factor.point_processes import HomogeneousPoissonPointProcess from structure_factor.spatial_windows import BoxWindow from structure_factor.structure_factor import StructureFactor from structure_factor.tapers import multi_sinetaper_grid from structure_factor.utils import meshgrid_to_column_matrix point_process = HomogeneousPoissonPointProcess(intensity=1) window = BoxWindow([[-50, 50], [-50, 50]]) point_pattern = point_process.generate_point_pattern(window=window) sf = StructureFactor(point_pattern) # Use the family of sine tapers x = np.linspace(-2, 2, 80) x = x[x != 0] k = meshgrid_to_column_matrix(np.meshgrid(x, x)) tapers = multi_sinetaper_grid(point_pattern.dimension, p_component_max=2) k, sf_estimated = sf.tapered_estimator(k, tapers=tapers, debiased=True, direct=True) sf.plot_non_isotropic_estimator( k, sf_estimated, plot_type="all", error_bar=True, bins=30, label=r"$\widehat{S}_{\mathrm{MDDTP}}((t_j)_1^4, \mathbf{k})$", ) plt.tight_layout(pad=1)
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
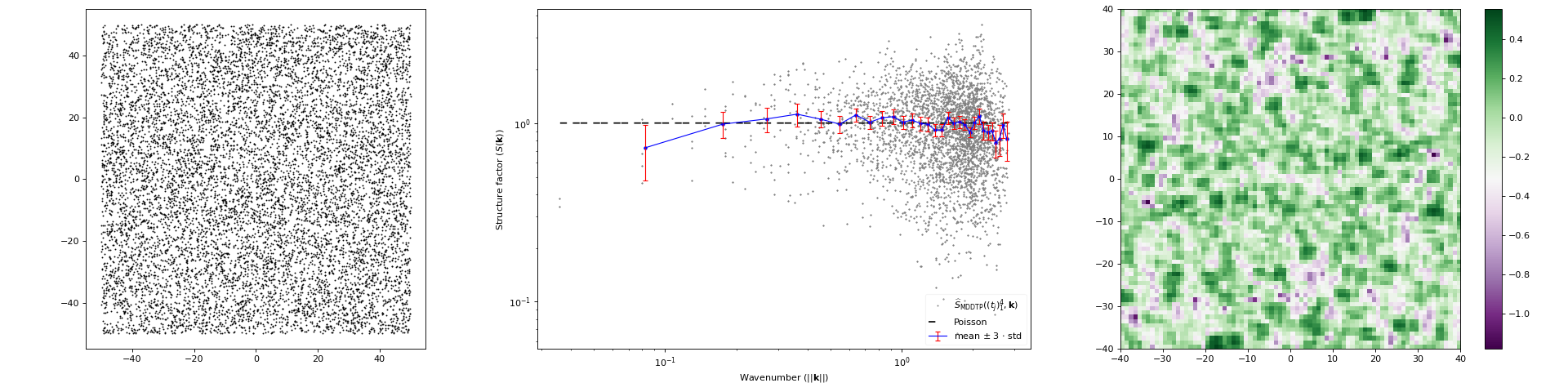 Definition
DefinitionThe tapered estimator \(\widehat{S}_{\mathrm{TP}}(t, k)\), is an estimator of the structure factor \(S\) of a stationary point process \(\mathcal{X} \subset \mathbb{R}^d\) with intensity \(\rho\). It is computed from one realization \(\mathcal{X}\cap W =\{\mathbf{x}_i\}_{i=1}^N\) of \(\mathcal{X}\) within a box window \(W\).
\[\widehat{S}_{\mathrm{TP}}(t, \mathbf{k}) = \frac{1}{\rho} \left\lvert \sum_{j=1}^N t(x_j, W) \exp(- i \left\langle k, x_j \right\rangle)\right\rvert^2,\]If several tapers are used, a simple average of the corresponding tapered estimators is computed. The resulting estimator is call multitapered estimator.
\[\widehat{S}_{\mathrm{MTP}}((t_{q})_{q=1}^P, \mathbf{k}) = \frac{1}{P}\sum_{q=1}^{P} \widehat{S}(t_{q}, \mathbf{k})\]where, \((t_{q})_{q}\) is a family of tapers supported on the observation window (satisfying some conditions), \(P\) is the number of tapers used, and \(k \in \mathbb{R}^d\). For more details, we refer to [HGBLachiezeR22], (Section 3.1).
Note
Typical usage
If the observation window is not a
BoxWindow, use the methodrestrict_to_window()to extract a sub-sample in aBoxWindow.
See also
multitapered_estimator()
- bartlett_isotropic_estimator(k_norm=None, **params)[source]
Compute Bartlett’s isotropic estimator \(\widehat{S}_{\mathrm{BI}}\) from one realization of an isotropic point process encapsulated in the
point_patternattribute.- Parameters
k_norm (numpy.ndarray, optional) – Array of wavenumbers of size \(n\) where the estimator is to be evaluated. Defaults to None.
- Keyword Arguments
params (dict) – Keyword argument
nb_valuesofallowed_k_norm_bartlett_isotropic used when ``k_norm=None`()to specify the number of allowed wavenumbers to be considered.- Returns
k_norm: Wavenumber(s) on which Bartlett’s isotropic estimator has been evaluated.
estimation: Evaluation(s) of Bartlett’s isotropic estimator at
k.
- Return type
tuple(numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray)
Example
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from structure_factor.point_processes import HomogeneousPoissonPointProcess from structure_factor.spatial_windows import BallWindow from structure_factor.structure_factor import StructureFactor from structure_factor.tapered_estimators_isotropic import ( allowed_k_norm_bartlett_isotropic, ) point_process = HomogeneousPoissonPointProcess(intensity=1) window = BallWindow(center=[0, 0], radius=50) point_pattern = point_process.generate_point_pattern(window=window) sf = StructureFactor(point_pattern) d, r = point_pattern.dimension, point_pattern.window.radius k_norm = allowed_k_norm_bartlett_isotropic(dimension=d, radius=r, nb_values=60) k_norm, sf_estimated = sf.bartlett_isotropic_estimator(k_norm) ax = sf.plot_isotropic_estimator( k_norm, sf_estimated, label=r"$\widehat{S}_{\mathrm{BI}}(k)$" ) plt.tight_layout(pad=1)
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
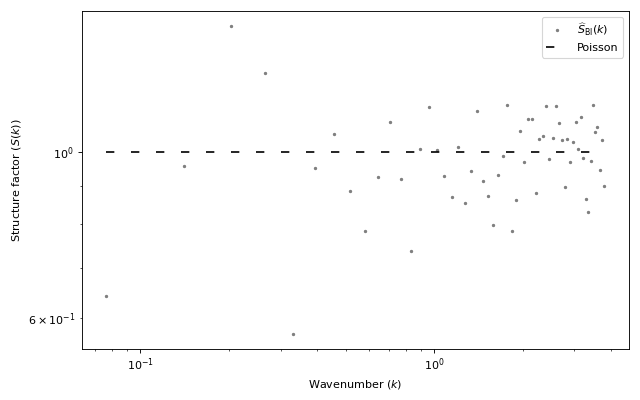 Definition
DefinitionBartlett’s isotropic estimator \(\widehat{S}_{\mathrm{BI}}\) is an estimator of the structure factor \(S\) of a stationary isotropic point process \(\mathcal{X} \subset \mathbb{R}^d\) with intensity \(\rho\). It is computed from one realization \(\mathcal{X}\cap W =\{\mathbf{x}_i\}_{i=1}^N\) of \(\mathcal{X}\) within a ball window \(W=B(\mathbf{0}, R)\).
\[\begin{split}\widehat{S}_{\mathrm{BI}}(k) = 1 + \frac{ (2\pi)^{d/2} }{\rho |W| \omega_{d-1}} \sum_{ \substack{j, q =1 \\ j\neq q } }^{N } \frac{1}{(k \|\mathbf{x}_j - \mathbf{x}_q\|_2)^{d/2 - 1}} J_{d/2 - 1}(k \|\mathbf{x}_j - \mathbf{x}_q\|_2).\end{split}\]For more details, we refer to [HGBLachiezeR22], (Section 3.2).
Note
Typical usage
If the observation window is not a
BallWindow, use the methodrestrict_to_window()to extract a sub-sample in aBallWindow.
- quadrature_estimator_isotropic(pcf, k_norm=None, method='BaddourChouinard', **params)[source]
Approximate the structure factor of a stationary isotropic point process at values
k_norm, given its pair correlation functionpcf, using a quadraturemethod.Warning
It only applies to point processes in even dimension \(d\), due to evaluations of the zeros of Bessel functions of order \(d / 2 - 1\) that must integer-valued.
- Parameters
pcf (callable) – Pair correlation function.
k_norm (numpy.ndarray, optional) – Vector of wavenumbers (i.e., norms of wavevectors) where the structure factor is to be evaluated. Optional if
method="BaddourChouinard"(since this method evaluates the Hankel transform on a specific set of wavenumbers), but it is non optional ifmethod="Ogata". Defaults to None.method (str, optional) –
Trigger the use of
"BaddourChouinard"or"Ogata"quadrature to estimate the structure factor. Defaults to"BaddourChouinard",if
"BaddourChouinard": The Hankel transform is approximated using the Discrete Hankel transform [BC15]. SeeHankelTransformBaddourChouinardif
"Ogata": The Hankel transform is approximated using Ogata quadrature [Oga05]. SeeHankelTransformOgata
- Keyword Arguments
params (dict) –
Keyword arguments passed to the corresponding Hankel transformer selected according to the input argument
method.method == "Ogata", seecompute_transformation_parameters()step_sizenb_points
method == "BaddourChouinard", seecompute_transformation_parameters()r_maxnb_pointsinterpolotationdictionnary containing the keyword arguments of scipy.integrate.interp1d parameters.
- Returns
k_norm: Vector of wavenumbers.
estimation: Evaluations of the structure factor on
k_norm.
- Return type
tuple (numpy.ndarray, numpy.ndarray)
Example
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import structure_factor.pair_correlation_function as pcf from structure_factor.point_processes import HomogeneousPoissonPointProcess from structure_factor.spatial_windows import BallWindow from structure_factor.structure_factor import StructureFactor point_process = HomogeneousPoissonPointProcess(intensity=1) window = BallWindow(center=[0, 0], radius=40) point_pattern = point_process.generate_point_pattern(window=window) pcf_estimated = pcf.estimate( point_pattern, method="fv", Kest=dict(rmax=20), fv=dict(method="c", spar=0.2) ) # Interpolate/extrapolate the results r = pcf_estimated["r"] pcf_r = pcf_estimated["pcf"] pcf_interpolated = pcf.interpolate(r=r, pcf_r=pcf_r, drop=True) # Estimate the structure factor using Baddour Chouinard quadrature sf = StructureFactor(point_pattern) k_norm = np.linspace(1, 10, 500) # vector of wavelength k_norm, sf_estimated = sf.quadrature_estimator_isotropic( pcf_interpolated, method="BaddourChouinard", k_norm=k_norm, r_max=20, nb_points=1000 ) fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 6)) fig = sf.plot_isotropic_estimator( k_norm, sf_estimated, axis=ax, error_bar=True, bins=30, label=r"$\widehat{S}_{\mathrm{BC}}(k)$", ) plt.tight_layout(pad=1)
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
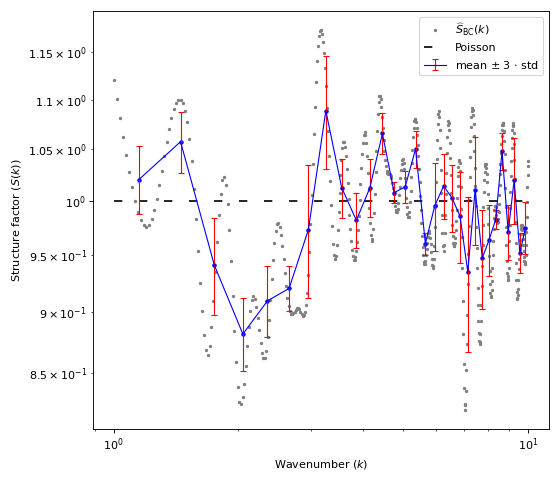 Definition
DefinitionThe structure factor \(S\) of a stationary isotropic point process \(\mathcal{X} \subset \mathbb{R}^d\) with intensity \(\rho\), can be defined via the Hankel transform \(\mathcal{H}_{d/2 -1}\) of order \(d/2 -1\) as follows,
\[S(\|\mathbf{k}\|_2) = 1 + \rho \frac{(2 \pi)^{d/2}}{\|\mathbf{k}\|_2^{d/2 -1}} \mathcal{H}_{d/2 -1}(\tilde g -1)(\|\mathbf{k}\|_2), \quad \tilde g: x \mapsto g(x) x^{d/2 -1},\]where, \(g\) is the pair correlation function of \(\mathcal{X}\).
This is a result of the relation between the Symmetric Fourier transform and the Hankel Transform. For more details, we refer to [HGBLachiezeR22], (Section 3.2).
Note
Typical usage
Estimate the pair correlation function using
estimate().Clean and interpolate/extrapolate the resulting estimation using
interpolate()to get a function.Use the result as the input
pcf.
See also
estimate()interpolate()
- plot_isotropic_estimator(k_norm, estimation, axis=None, scale='log', k_norm_min=None, exact_sf=None, color='grey', error_bar=False, label='$\\widehat{S}$', file_name='', **binning_params)[source]
Display the outputs of the method
quadrature_estimator_isotropic(), ortapered_estimator_isotropic().- Parameters
k_norm (numpy.ndarray) – Vector of wavenumbers (i.e., norms of wavevectors) on which the structure factor has been approximated.
estimation (numpy.ndarray) – Approximation(s) of the structure factor corresponding to
k_norm.axis (plt.Axes, optional) – Support axis of the plot. Defaults to None.
scale (str, optional) – Trigger between plot scales of see matplolib documentation. Defaults to ‘log’.
k_norm_min (float, optional) – Estimated lower bound of the wavenumbers. Defaults to None.
exact_sf (callable, optional) – Theoretical structure factor of the point process. Defaults to None.
error_bar (bool, optional) – If
True,k_normand correspondinglyestimation, are divided into sub-intervals (bins). Over each bin, the mean and the standard deviation ofsiare derived and visualized on the plot. Note that each error bar corresponds to the mean \(\pm 3 \times\) standard deviation. To specify the number of bins, add it as a keyword argument. For more details see_bin_statistics(). Defaults to False.file_name (str, optional) – Name used to save the figure. The available output formats depend on the backend being used. Defaults to “”.
- Keyword Arguments
binning_params – (dict): Used when
error_bar=True, by the methodutils_bin_statistics()as keyword arguments (except"statistic") of scipy.stats.binned_statistic.- Returns
Plot of the approximated structure factor.
- Return type
plt.Axes
- plot_non_isotropic_estimator(k, estimation, axes=None, scale='log', plot_type='radial', positive=False, exact_sf=None, error_bar=False, label='$\\widehat{S}$', rasterized=True, file_name='', window_res=None, **binning_params)[source]
Display the outputs of the method
scattering_intensity(),tapered_estimator().- Parameters
k (numpy.ndarray) – Wavevector(s) on which the scattering intensity has been approximated. Array of size \(n \times d\) where \(d\) is the dimension of the space, and \(n\) is the number of wavevectors.
estimation (numpy.ndarray) – Approximated structure factor associated to k.
axes (plt.Axes, optional) – Support axes of the plots. Defaults to None.
scale (str, optional) –
Trigger between plot scales of see matplolib documentation. Defaults to “log”.
plot_type (str, optional) –
Type of the plot to visualize, “radial”, “imshow”, or “all”. Defaults to “radial”.
If “radial”, the output is a 1D plot of estimation w.r.t. the norm(s) of k.
If “imshow” (option available only for a 2D point process), the output is a 2D color level plot.
If “all” (option available only for a 2D point process), the result contains 3 subplots: the point pattern (or a restriction to a specific window if
window_resis set), the radial plot, and the color level plot. Note that the options “imshow” and “all” couldn’t be used, ifkcouldn’t be reshaped as a meshgrid.
positive (bool, optional) – If True, consider only the positive values of estimation. Defaults to False.
exact_sf (callable, optional) – Theoretical structure factor of the point process. Defaults to None.
error_bar (bool, optional) – If
True,k_normand correspondinglyestimation, are divided into sub-intervals (bins). Over each bin, the mean and the standard deviation ofestimationare derived and visualized on the plot. Note that each error bar corresponds to the mean \(\pm 3 \times\) standard deviation. To specify the number of bins, add it as a keyword argument. For more details see_bin_statistics(). Defaults to False.rasterized (bool, optional) – Rasterized option of matlplotlib.plot. Defaults to True.
file_name (str, optional) – Name used to save the figure. The available output formats depend on the backend being used. Defaults to “”.
window_res (
AbstractSpatialWindow, optional) – New restriction window. Useful when the sample of points is large and “plt_type=’all’”, so for time and visualization purposes, it is better to restrict the plot of the point process to a smaller window. Defaults to None.
- Keyword Arguments
binning_params (dict) –
Used when
error_bar=True, by the method_bin_statistics()as keyword arguments (except"statistic") of scipy.stats.binned_statistic.- Returns
Plot of the approximated structure factor.
- Return type
plt.Axes